I will be presenting a couple of talks in October this year – my first lecture is about Regency Fashion – my second lecture is a entertaining, lively and informative Tudor Talk with Costume Display for the Quilters Guild on 12 October 2019.
I am demonstrating the design and construction of my handmade reproduction gowns and also a brief history of the people who wore them. I will also include reproduction underwear so thought it would be an opportune time to give a brief outline of the underclothes I will be showing at my Tudor talk.
The Chemise
The first layer for everyone high or low was the chemise also called a “smock” or “shift” in the 16th century, which was a simple garment was worn next to the skin to protect clothing from sweat and body oils. As Elizabethans rarely indulged in full-body baths, and as the clothing of the middle and upper classes was not the kind one could pound on a river rock or scrub regularly with ashes and lye soap, the chemise was vital to Elizabethan costume.
Smocks were made of fine linen, as fine as the wearer could afford. Many of the better smocks were made of what we now call “handkerchief-weight” linen. Lawn, cypress and holland were three 16th c. varieties of sheer linen used for fine smocks. These smocks hung to just about knee to calf-length, on average. This is a low-necked gathered smock – it has a very voluminous body and sleeves, I have gathered the fabric into a low neckband and wristbands. It was sometimes pulled through the slashing of the outer garments during this period.Resistance to fungus and bacteria – Linen has natural antibacterial properties and that is why it is used in medicine. It also acts against the bacteria that make you smell.
The Corset
Over the chemise was worn the corset – my corset has been inspired by the corset found on the ‘effigy’ of Elizabeth the First (below).
I have designed a tabbed waist corset, which is the type which is the easiest to wear. The tabs distribute pressure so the corset does not ‘dig in’ at the waist. The Elizabethan corset gave a period shape to the body and sometimes had straps to help lift the breasts.
It was made of linen (I have constructed it in cotton twill or linen. Spring steel boning has been inserted into channels to give strength. During the 16th century corsets were stiffened with whalebone, reeds, steel or rope. I have used binding on the edges as Elizabeth’s corset was bound with leather. The lacing holes are reinforced with sturdy cotton thread and the corset is laced with cord. The corset was worn over the chemise to save it from perspiration so it didn’t have to be washed too often.
The Spanish Farthingale or Hoop Skirt
To create the correct shape for clothes of the period a Spanish Farthingale was worn. This was a bell-shaped hoop skirt worn under the skirts of well-to-do women during the Tudor and Elizabethan era. From 1530 to 1580, the farthingale played an important part in shaping the fashionable silhouette.(First Farthingale worn by Joan of Portugal to hide pregnancy – had two illegitimate children)
The Spanish Farthingale, as its name suggests, originated in Spain. Tradition holds that the Spanish Farthingale arrived in England in the 1520s, introduced by Katharine of Aragon, Henry VIII’s future queen. It is true that, beginning in the 1530s, clear evidence of hoop skirts worn by English noblewomen begin to appear in court paintings and portraits.
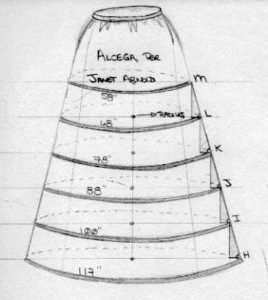
The pattern for this farthingale is from Juan de Alcega’s Tailor’s Pattern Book, published in 1589. It has been created from sections of calico – which are cut and then pieced together. The sections of fabric are placed so that no bias seams are sewn to each other. This was to eliminate the sagging which two bias seams sewn together would inevitably experience. I have cut additional pieces of fabric, 2 inches wide, to match the length of each piece of boning to create casings for the stiffening. After everything is sewn together, the farthingale would have been gathered at the top and the raw edges bound with a strip of fabric. It is reasonable to say that the opening would have been in the back or in the front for a front-lacing corset.
Three materials were known to be used for stiffening farthingales in Elizabeth’s time: rope, bent rope, and whalebone. Most recreation farthingales are made using hoop skirt boning. Hoop skirt boning is 1/2 inch wide stiffened canvas or plastic with spring steel along the edges. It is very stiff and can hold out the heaviest of skirts, yet is lighter than other boning materials. After the boning is inserted the casings are tacked close. The boning can however be easily removed so the farthingale can be washed.
The Bum roll
A Bumroll, which, as its name suggests, was a roll tied around the bum, was an essential piece of Tudor and Elizabethan underwear. In Elizabethan times, it was more commonly called a “roll”; “bumroll” is the modern term for the item.A bumroll is made from a crescent shape of non stretchy fabric such as calico which is stuffed with wadding and has ties attached to the ends.
The first hard evidence of a separate roll worn around the hips are a reference to them in Elizabeth’s wardrobe accounts from 1580. It was tied around the hips to make a woman’s skirt swell out becomingly at the waistline before falling to the ground. It was used throughout the 16th century and into the 17th, and considered an essential aid to fashionable dress.
- Without the foundation garments the shape of the dress of the period would be unable to be achieved so it is a very important part of the costumes.
- No type of panties or knickers were worn at this time -the first type of this type of underwear were in a form of leggings or long drawers, they originated in France in the early 19th century, and quickly spread to Britain and America.
- “Tudor clothing was time-consuming to don and doff, stiff, heavy, hot, never comfortable, never really clean and probably never free of accumulated body odours and the perfumes to mask them. Patterned with decorative stitching, heavy with embroidery, jewels and trumpery, over garments lay layer upon layer over corsets, shifts, bodices and other undergarments, some exaggerating the body’s natural shape, others camouflaging it.”
Although you would probably looked splendid in the 16th Century Court Fashions they certainly were I am sure you’ll agree not the most comfortable to wear or to wash!